What’s an Atom?
An atom:
- is the smallest particle of an element that can exist
- has the element’s chemical properties and,
- can take part in a chemical reaction.
In short, an atom is the smallest piece of an element that can unite with another atom of the same or different element to make a new substance. The ability of atoms to combine with one another in different amounts is one way nature can make so many different materials with unique physical and chemical properties.
Who Proposed the Idea of Atom?
Democritus was a famed Greek philosopher who proposed the idea of an atom.
How did Democritus Come up with the Idea of an Atom?
He imagined that if he slowly chopped a piece of solid metal block he will eventually reach a basic particle from which the solid metal block was made. It was this basic particle Democritus called an Atom, which means indivisible in Greek. As you can tell, his reasoning for an atom can be applied to any substance that exists in nature. The interesting thing was that Democritus had no experimental evidence to back his thinking. As a result, his idea of an atom was not widely accepted by other philosophers that lived during his time.
What Evidence Supports the Idea of An Atom?
Hundreds of years after Democritus’ idea of an atom, scientists had observed that when chemicals react with one another in an air tight vessel, the mass of the chemicals before they react was always equal to the mass of the chemicals after they react. In short, the mass of chemicals before reaction was always equal to the mass of chemicals after the reaction. This observation which was consistent with the experiments was later turned into a law called the law of conservation of mass. For simplicity, the mass of chemicals before reaction was called the mass of reactants and the mass of chemicals after the reaction was called the mass of products. We can rewrite the law of conservation of mass as: mass of reactants = (equal to) mass of products before and after a chemical reaction. Keep in mind that the term “products” refer to the new chemicals made from the reactants (starting chemicals).
Dalton and the Atomic Theory
Dalton, who is often called the father of chemistry, proposed the first atomic theory based on the experimental evidence that supported the law of conservation of mass. As you can tell, the word atomic came from Democritus idea of an atom. To see how the atomic theory evolved click here.
What Model is Used to Depict an Atom?
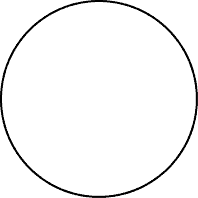
For simplicity, scientists use a circle or a fuzzy cloud to serve as a model of an atom; Be aware that this is just a model not an actual atom.

What Simple Activity Can You Do to Verify the Law of Conservation of Mass?
Use
- baking soda
- vinegar
- balloon
- test tube (any container suitable container)
- scale
to test the law of conservation of mass.
Check your understanding
- If you do not use the balloon in your experiment, will the mass of the chemicals remain the same before and after the reaction? Explain.