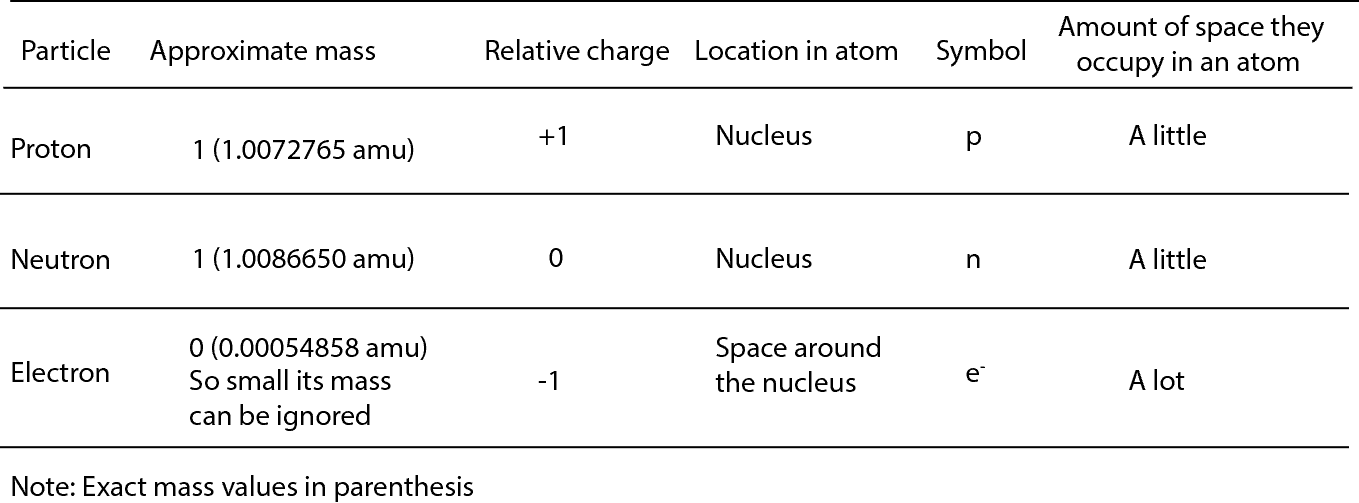
The subatomic particles are: protons, neutrons and electrons. And they are related to one another by their mass and charge. The properties of these particles are summarized in the table below.
In nature, an important rule is that positive charged particles always attract negative charged particles, and negative charged particles always repel negative charged particles, and positive charged particles always repel positive charged particles. This rule is summarized as unlike charges attract, while like charges repel. So,
Why does an atom stay together?
It stays together because the positively charged nucleus always attracts the negatively charged electron.
From the table, the mass of an electron is so small that it is assigned a value of zero. The amu you see attached to the exact mass values is called the atomic mass unit. The atomic mass unit is different from other units of measurement because it is developed by comparing the mass of atoms to the mass of Carbon-12 (an atom of carbon). As a result, these masses are always called relative atomic masses.
Can an atom be electrically neutral?
Yes! Since electrons carry a negative charge and protons a positive charge, when you have an equal number of each in an atom, their charges simply cancel each other out, making the atom neutral. However, when electrons are added or removed from a neutral atom, the atom becomes an ion and its no longer neutral because you now have unequal number of protons and electrons.