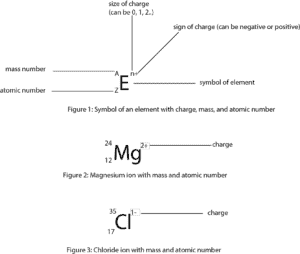
How to calculate the number of electrons in a positive ion
To calculate the number of electrons in an ion that carries a positive charge, you must recall that when an ion carries a positive charge, the number of electrons are fewer than the number of protons. So to get the number of electrons, you must subtract the size of charge (which is often written as a superscript on the right side of the symbol) from the atomic number or proton number. Let’s use figure 2 as an example. As you can see, Mg has an atomic number of 12 and a charge of +2, so to get the number of electrons for Mg ion, we must subtract 2 from the atomic number. Thus, 12-2= 10 electrons.
How to calculate the number of electrons in a negative ion (anion)
Likewise, to calculate the number of electrons for an ion that carries a negative charge, you must recall that when an ion carries a negative charge, the number of electrons are more than the number of protons. So to get the number of electrons, you must add the size of charge to the atomic or proton number. So from figure 3, the number of electrons for chloride ion is 17 + 1 = 18 electrons.
To learn how atoms form ions, click here.
To learn more about subatomic particles, click here
To learn why a cation is smaller than its neutral atom, click here