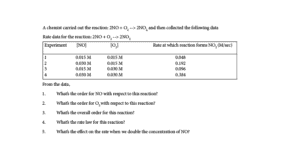
1. What’s the order for NO with respect to this reaction?
Strategy
From the data, carefully look for two different experiments in which the concentration of one reactant stays the same, while the concentration of the other reactant we want to study changes. So, if we want to determine how the concentration of NO affects the reaction rate, we must pick experiment 1 and 2 or experiment 3 and 4. In these experiments, the concentration of NO changes, while that of O2 remains unchanged.
If we pick experiment 1 and 2, you will notice that as the concentration of NO doubles from 0.015 M to 0.030 M, the rate at which NO2 forms quadruples. How did we determine that? We divided the rate at which NO2 forms in experiment 2 by its rate from experiment 1. Thus, 0.192/0.048 = 4. Which is the same as multiplying the rate from experiment 1 by 4 to get the rate in experiment 2(0.048 x 4 = 0.192). Therefore, the reaction order for NO is 2.
Similarly, you will get the same answer if you use experiment 3 and 4.
2. What’s the order for O2 with respect to this reaction?
From the data, you will notice that from experiment 1 and 3, the concentration of NO remains unchanged, while that of O2 changes.
Therefore, if you examine the data, for experiment 1 and 3, you will notice that as the concentration of O2 doubles from 0.015 M in experiment 1 to 0.030 M in experiment 2, the rate at which NO2 forms doubles. We got this by dividing the rate from experiment 3 by the rate from experiment 1. Thus, 0.096/0.048 = 2. Which is the same as multiplying the rate from experiment 1 by 2(0.048 x 2 = 0.096). Therefore, the reaction order for O2 is 1.
3. What’s the overall order for this reaction?
To get the overall order for this reaction, we sum the orders from the two reactants in the reaction. If we do, the answer is 2 + 1 = 3.
4. What’s the rate law for this reaction?
The rate law is R = k[NO]2 [O2]1
5. What’s the effect on the reaction rate when we double the concentration of NO?
Since from the rate law, the order of NO is 2. It means that when the concentration of NO doubles, the reaction rate quadruples.