Chemical reactions that can generate electricity are called REDOX reactions. REDOX reactions occur in the batteries you usually buy to power your electronic devices. REDOX reactions consist of two types of reactions. One is called reduction, while the other is called oxidation. When you combine the Red part of reduction to the Ox part of oxidation, you will get the acronym REDOX, which means reduction and oxidation reactions. Why do these reactions generate electricity? If you consider electricity simply to be the flow of electrons, then you can say that in REDOX reactions some chemicals are naturally inclined to lose electrons while others are naturally inclined to accept electrons. As a result, when these chemicals are kept in separate containers and connected by a wire, electrons usually flow through the wire from one chemical to the other, producing electricity as a result.
What is reduction in redox reactions?
When an atom accepts an electron, chemists usually say that the atom has undergone reduction. Another way of saying the same thing is that the atom has been reduced. Therefore, REDUCTION is defined as the gain of electrons.
What is oxidation in redox reactions?
When an atom loses an electron, chemists usually say that the atom has undergone oxidation. Another way of saying the same thing is that the atom has been oxidized. Therefore, OXIDATION is defined as the loss of electrons.
As you can tell, in redox reactions, reduction cannot occur without oxidation and oxidation cannot occur without reduction. Thus, the two reactions must occur together to generate electricity. For this reason, REDOX reactions are sometimes called electron transfer reactions.
An example of a redox reaction includes:
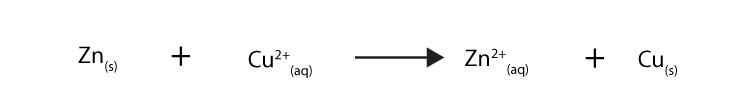
Now, from the equation above, how can you tell that electrons are being transferred as reactants turn into products? Since the chemical equation includes the charges of the chemicals, you can tell by tracking how the charges of each chemical are changing on the reactants and products side of the chemical equation.
For instance, since the charge of Zn goes from neutral to +2, it follows that Zn must have lost two electrons. And since the charge of Cu goes from +2 to neutral (0), it follows that Cu must have gained two electrons. Therefore, you can say that Zn has been oxidized to Zn2+ by losing two electrons, while Cu2+has been reduced to Cu by gaining two electrons.
Now, imagine that you have been given the following balanced chemical equation:
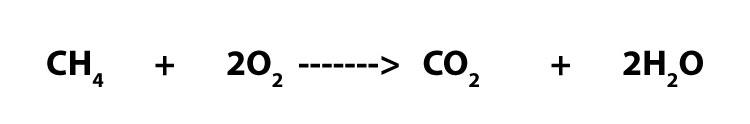
How do you tell that electron transfer is occurring? As you can see, unlike the previous one, the chemicals in this equation are all neutral molecules. This means that it will be difficult to tell without you doing a little bit of electron bookkeeping. To learn more about this electron bookkeeping, click here.