What is Atomic number?
Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It can also be the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Pay attention to the word neutral. The proton number is so important that it is used to identify an element. As a result, all the elements on the periodic table (an organized table of elements) are arranged based on increasing atomic number. So as you move from left to right on the periodic table the atomic number of the elements increase step-by-step.
What’s Neutron number?
Neutron number is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
What’s Mass number?
Mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. As you can tell, the number of electrons are not included in the mass number, which means that the mass number is not the same thing as the mass of the atom (atomic mass). If you know the mass number and atomic number, you can always find the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
What symbols are used to describe an atom?
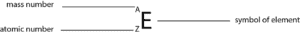
The chemical symbol of the element is represented by the letter E. The mass number (superscript, A) and the atomic number (subscript, Z) appear on the left hand side of the chemical symbol. These symbols vary from element to element. Now, let’s apply these concepts to complete the following table

From the table, you are given the atomic and mass number of Mg and the mass number of Kr. To complete the first row on the table, you have to remember that the proton number is the subscript on the left side of the chemical symbol and is the same as the atomic number. And since the atom is neutral, the number of electrons and protons are equal. For Kr, you have to look for its atomic number from the Periodic Table.
From the periodic table, the atomic number of Kr is 36. Therefore to get the number of neutrons, you must subtract the atomic number (36) from the mass number ( 84). The last two rows have no chemical symbols, therefore, you must use their atomic numbers to identify the elements on the periodic table. To get the atomic number for the last row, you must remember that since the atom is neutral, the number of electrons are the same as the number protons.
How do you know an atom is neutral?
Sometimes you can deduce by checking whether the number of electrons are the same as the number of protons. In our example you don’t have to do that because I already wrote under the table that all the elements are neutral. Thus, the number of protons is 6. To get the mass number, you must add the number of protons to the number of neutrons. Here is the completed table:
What’re isotopes?
From the table, you can see that both carbon atoms have an atomic number of 6 but a mass number of 6 and 7. Why is that? Is so because in nature you can have an element that consists of atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons. When this happens, we usually call the different versions of the same element isotopes. So if we call them by their mass numbers, we will say carbon-12 (read as carbon twelve) and carbon-13 are isotopes of carbon, and they have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
To learn how atoms form ions, click here.