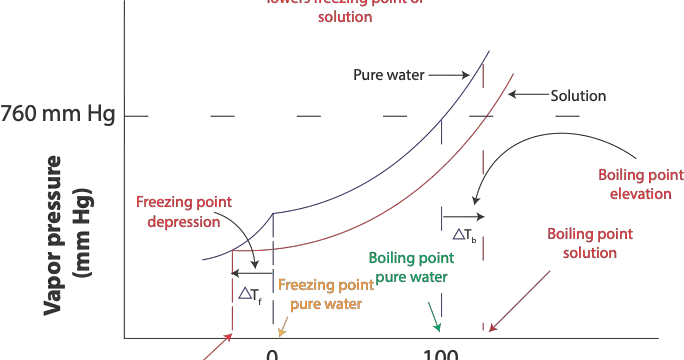
When the vapor pressure of pure water is equal to standard atmospheric pressure (1 atm or 760 mm Hg) at 100 ºC pure water will boil at 100 ºC, which is its normal boiling point. However, since the …
What is colligative property vapor pressure lowering and how do you calculate it using Raoult’s law?
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapor above a liquid in a closed container when the rate of evaporation of the liquid is equal to the rate of condensation of its vapor. However, vapor …
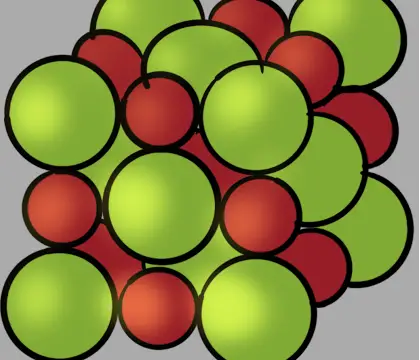
How to determine total atoms in unit cell to calculate mass and density of the unit cell
The particles in crystalline solids are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern held together by attractive forces between the particles. This orderly arrangement forms a three-dimensional structure …
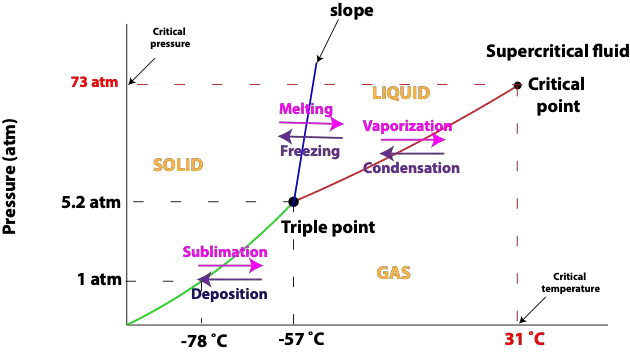
How to interpret and analyze a phase diagram
A phase diagram is a plot of pressure versus temperature that shows the phase (state) of a substance under differing conditions of temperature and pressure. Pressure and temperature can have an …
Continue Reading about How to interpret and analyze a phase diagram →
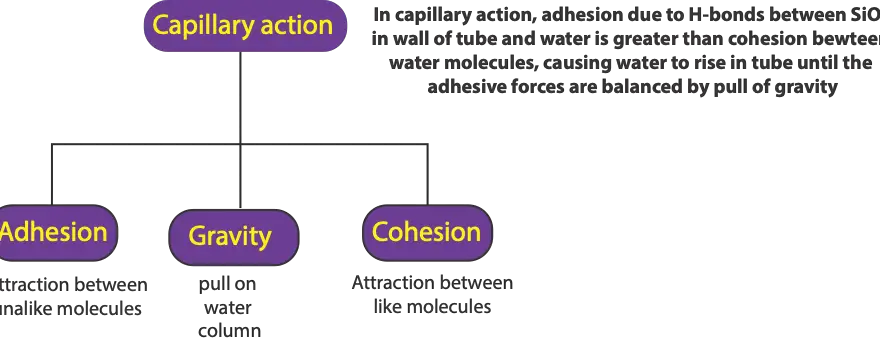
What is capillary action, and which three types of forces are responsible?
Capillary action is when water rises in a small glass tube because of the attraction between molecules of silicon dioxide (SiO2) in walls of glass tube and water (H2O) molecules. This attraction …
Continue Reading about What is capillary action, and which three types of forces are responsible? →
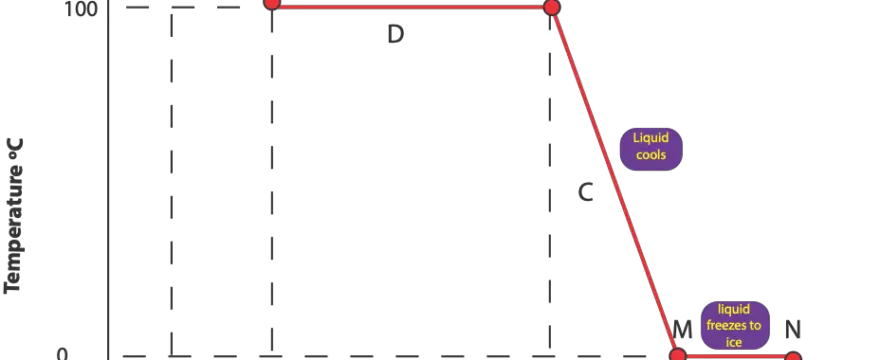
What happens to water vapor as temperature decreases or as it cools?
As temperature decreases, molecules of water vapor move a lot less. That is the kinetic energy of water molecules in water vapor decreases until such a point that these molecules no longer have enough …
Continue Reading about What happens to water vapor as temperature decreases or as it cools? →